Do You Really Understand Heel Soreness?
Overview

Heel pain is one of the most common conditions treated by podiatrists. It is often a message from the body that something is in need of medical attention. Pain that occurs right after an injury or early in an illness may play a protective role, often warning us about the damage we have suffered. The greatest incidence of heel pain is seen in middle-aged men and women. It is also seen in those who take part in regular sporting activities and those significantly overweight and on their feet a lot. Heel pain can also occur in children, usually between 8 and 13, as they become increasingly active in sporting activities.
Causes
Heel pain has many causes. Heel pain is generally the result of faulty biomechanics (walking gait abnormalities) that place too much stress on the heel bone and the soft tissues that attach to it. The stress may also result from injury, or a bruise incurred while walking, running, or jumping on hard surfaces; wearing poorly constructed footwear (such as flimsy flip-flops); or being overweight.
Symptoms
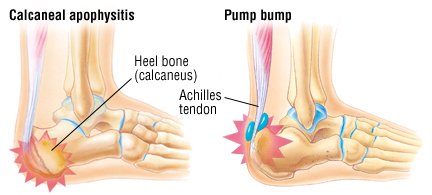
Both heel pain and heel spurs are frequently associated with an inflammation of the long band of tissue that connects the heel and the ball of the foot. The inflammation of this arch area is called plantar fasciitis. The inflammation maybe aggravated by shoes that lack appropriate support and by the chronic irritation that sometimes accompanies an athletic lifestyle. Achilles Tendinopathy, Pain and inflammation of the tendon at the back of the heel that connects the calf muscle to the foot. Sever?s, Often found in children between the ages of 8 - 13 years and is an inflammation of the calcaneal epiphyseal plate (growth plate) in the back of the heel. Bursitis, An inflamed bursa is a small irritated sack of fluid at the back of the heel. Other types of heel pain include soft tissue growths, Haglunds deformity (bone enlargement at the back of the heel), bruises or stress fractures and possible nerve entrapment.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of heel pain and heel spurs is made by a through history of the course of the condition and by physical exam. Weight bearing x-rays are useful in determining if a heel spur is present and to rule out rare causes of heel pain such as a stress fracture of the heel bone, the presence of bone tumors or evidence of soft tissue damage caused by certain connective tissue disorders.
Non Surgical Treatment
Most patients get better with the help of nonsurgical treatments. Stretches for the calf muscles on the back of the lower leg take tension off the plantar fascia. A night splint can be worn while you sleep. The night splint keeps your foot from bending downward. It places a mild stretch on the calf muscles and the plantar fascia. Some people seem to get better faster when using a night splint. They report having less heel pain when placing the sore foot on the ground in the morning. There have been a few studies that reported no significant benefit from adding night splinting to a program of antiinflammatory meds and stretching. Other studies report the benefits of short-term casting to unload the heel, immobilize the plantar fascia, and reduce repetitive microtrauma. Supporting the arch with a well fitted arch support, or orthotic, may also help reduce pressure on the plantar fascia. Placing a special type of insert into the shoe, called a heel cup, can reduce the pressure on the sore area. Wearing a silicone heel pad adds cushion to a heel that has lost some of the fat pad through degeneration. Shock wave therapy is a newer form of nonsurgical treatment. It uses a machine to generate shock wave pulses to the sore area. Patients generally receive the treatment once each week for up to three weeks. It is not known exactly why it works for plantar fasciitis. It's possible that the shock waves disrupt the plantar fascial tissue enough to start a healing response. The resulting release of local growth factors and stem cells causes an increase in blood flow to the area. Recent studies indicate that this form of treatment can help ease pain, while improving range of motion and function.
Surgical Treatment
When a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is made early, most patients respond to conservative treatment and don?t require surgical intervention. Often, when there is a secondary diagnosis contributing to your pain, such as an entrapped nerve, and you are non-responsive to conservative care, surgery may be considered. Dr. Talarico will discuss all options and which approach would be the most beneficial for your condition.
How do you treat heel pain?
Prevention
Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. Losing weight, and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet, can be beneficial for your feet. Wearing appropriate footwear is also important. Ideally, you should wear shoes with a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels.

Heel pain is one of the most common conditions treated by podiatrists. It is often a message from the body that something is in need of medical attention. Pain that occurs right after an injury or early in an illness may play a protective role, often warning us about the damage we have suffered. The greatest incidence of heel pain is seen in middle-aged men and women. It is also seen in those who take part in regular sporting activities and those significantly overweight and on their feet a lot. Heel pain can also occur in children, usually between 8 and 13, as they become increasingly active in sporting activities.
Causes
Heel pain has many causes. Heel pain is generally the result of faulty biomechanics (walking gait abnormalities) that place too much stress on the heel bone and the soft tissues that attach to it. The stress may also result from injury, or a bruise incurred while walking, running, or jumping on hard surfaces; wearing poorly constructed footwear (such as flimsy flip-flops); or being overweight.
Symptoms
Both heel pain and heel spurs are frequently associated with an inflammation of the long band of tissue that connects the heel and the ball of the foot. The inflammation of this arch area is called plantar fasciitis. The inflammation maybe aggravated by shoes that lack appropriate support and by the chronic irritation that sometimes accompanies an athletic lifestyle. Achilles Tendinopathy, Pain and inflammation of the tendon at the back of the heel that connects the calf muscle to the foot. Sever?s, Often found in children between the ages of 8 - 13 years and is an inflammation of the calcaneal epiphyseal plate (growth plate) in the back of the heel. Bursitis, An inflamed bursa is a small irritated sack of fluid at the back of the heel. Other types of heel pain include soft tissue growths, Haglunds deformity (bone enlargement at the back of the heel), bruises or stress fractures and possible nerve entrapment.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of heel pain and heel spurs is made by a through history of the course of the condition and by physical exam. Weight bearing x-rays are useful in determining if a heel spur is present and to rule out rare causes of heel pain such as a stress fracture of the heel bone, the presence of bone tumors or evidence of soft tissue damage caused by certain connective tissue disorders.
Non Surgical Treatment
Most patients get better with the help of nonsurgical treatments. Stretches for the calf muscles on the back of the lower leg take tension off the plantar fascia. A night splint can be worn while you sleep. The night splint keeps your foot from bending downward. It places a mild stretch on the calf muscles and the plantar fascia. Some people seem to get better faster when using a night splint. They report having less heel pain when placing the sore foot on the ground in the morning. There have been a few studies that reported no significant benefit from adding night splinting to a program of antiinflammatory meds and stretching. Other studies report the benefits of short-term casting to unload the heel, immobilize the plantar fascia, and reduce repetitive microtrauma. Supporting the arch with a well fitted arch support, or orthotic, may also help reduce pressure on the plantar fascia. Placing a special type of insert into the shoe, called a heel cup, can reduce the pressure on the sore area. Wearing a silicone heel pad adds cushion to a heel that has lost some of the fat pad through degeneration. Shock wave therapy is a newer form of nonsurgical treatment. It uses a machine to generate shock wave pulses to the sore area. Patients generally receive the treatment once each week for up to three weeks. It is not known exactly why it works for plantar fasciitis. It's possible that the shock waves disrupt the plantar fascial tissue enough to start a healing response. The resulting release of local growth factors and stem cells causes an increase in blood flow to the area. Recent studies indicate that this form of treatment can help ease pain, while improving range of motion and function.
Surgical Treatment
When a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is made early, most patients respond to conservative treatment and don?t require surgical intervention. Often, when there is a secondary diagnosis contributing to your pain, such as an entrapped nerve, and you are non-responsive to conservative care, surgery may be considered. Dr. Talarico will discuss all options and which approach would be the most beneficial for your condition.
How do you treat heel pain?
Prevention

Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. Losing weight, and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet, can be beneficial for your feet. Wearing appropriate footwear is also important. Ideally, you should wear shoes with a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels.